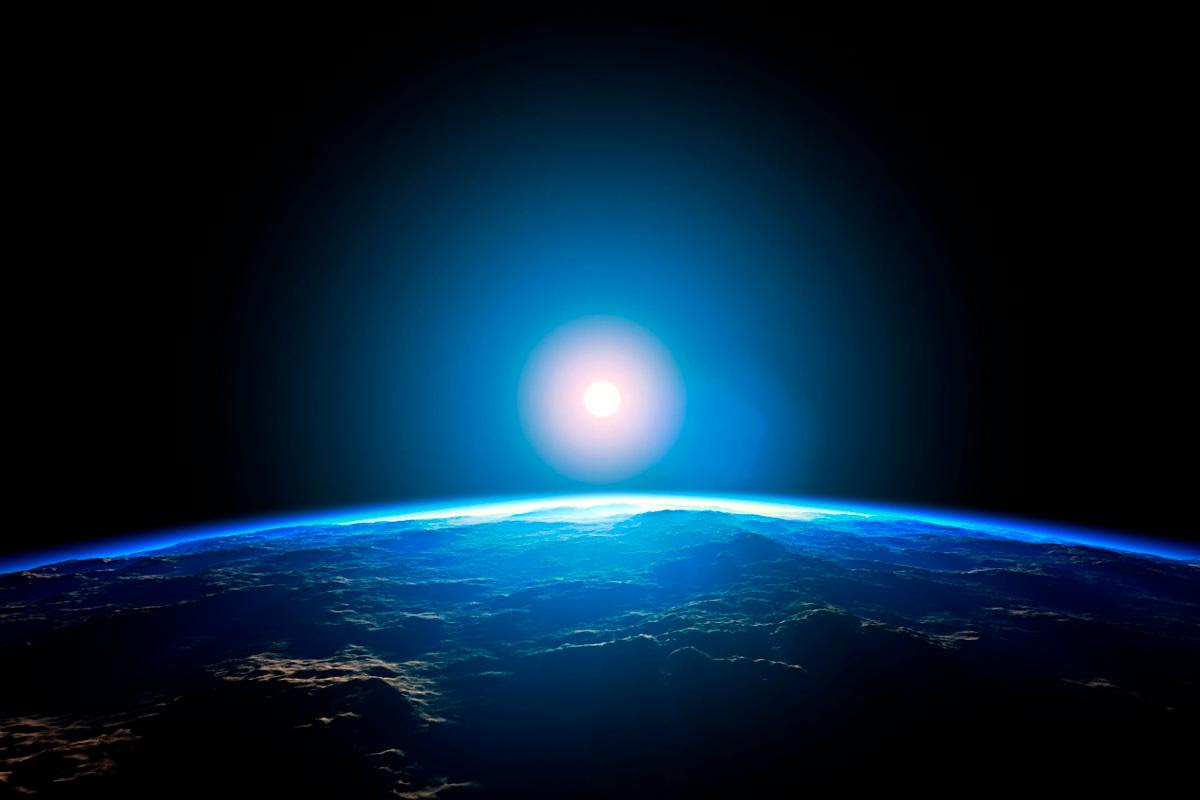
The layer of the atmosphere at rest has a structure of concentric layers. The photograph below shows the troposphere at the bottom, where the temperature decreases linearly with altitude, the stratosphere at the top, where the temperature rises due to the heat released by the absorption of ultraviolet radiation, and the transition to space at the top, which remains absolutely black.
Scientists explain that all the phenomena present in this atmosphere, and even beyond, come from the waves that cross it by sound and light.
Their respective capacities allow the images to reach us before the noises, the sky to turn blue in the middle of the day and to turn red in the evening.
Above the visible light, the Sun sends us all the fraction of its radiation directed towards the Earth, of which a part, the albedo, is reflected towards space before reaching the ground. Only the remainder, of the order of 240 W.m-2, reaches the ground and the average temperature of the planet, close to 15 °C, is such that its own radiation towards space balances this received radiation. Taking into account the greenhouse effect, the Earth must radiate 390 W.m-2 at ground level for 240W.m-2 to reach space.
|
ReplyForward
|



Comment here